使用公用表表达式 (CTE) 简化复杂查询
CTE 是命名的结果集,有助于保持代码的整洁。它们允许您在同一个查询中重用结果,并执行多级聚合。
公用表表达式 (CTE) 是 SQL 查询中一个有名称的结果集。CTE 有助于保持代码的整洁,并允许您对数据执行多级聚合,例如查找计数集中的平均值。我们将通过一些示例向您展示 CTE 的工作方式以及为什么会使用它们,并使用 Metabase 随附的 示例数据库,以便您可以跟随学习。
CTE 的好处
- CTE 使代码更易读。 可读性使查询更易于调试。
- CTE 可以在整个查询中多次引用结果。 通过存储子查询的结果,您可以在更大的查询中重用它们。
- CTE 可以帮助您执行多级聚合。 使用 CTE 存储聚合的结果,然后可以在主查询中对其进行汇总。
CTE 语法
CTE 的语法使用 WITH 关键字和一个变量名来创建一个临时表,您可以在查询的其他部分引用该表。
WITH cte_name(column1, column2, etc.) AS (SELECT ...)
这里的 AS 关键字有些不寻常。通常 AS 用于指定别名,例如 consumables_orders AS orders,其中 orders 是 AS 右侧的别名。对于 CTE,变量 cte_name 位于 AS 关键字的前面(左侧),后面跟着子查询。请注意,列列表 (column1, column2, etc) 是可选的,前提是 SELECT 语句中的每个列都有唯一的名称。
CTE 示例
让我们来看一个简单的例子。我们想看到所有 total 大于平均订单总数的订单列表。
SELECT
id,
total
FROM
orders
WHERE
-- filter for orders with above-average totals
total > (
SELECT
AVG(total)
FROM
orders
)
此查询返回
|ID |TOTAL |
|----|-------|
|2 |117.03 |
|4 |115.22 |
|5 |134.91 |
|... |... |
这似乎很简单:我们在计算平均订单总数的 WHERE 子句中嵌套了一个子查询 SELECT AVG(total) FROM orders。但是,如果获取平均值更复杂呢?例如,假设您需要过滤掉测试订单,或者排除您的应用程序启动之前的订单
SELECT
id,
total
FROM
orders
WHERE
total > (
-- calculate average order total
SELECT
AVG(total)
FROM
orders
WHERE
-- exclude test orders
product_id > 10
AND -- exclude orders before launch
created_at > '2016-04-21'
AND -- exclude test accounts
user_id > 10
)
ORDER BY
total DESC
现在查询开始变得难以理解。我们可以使用 WITH 语句将子查询重写为一个公用表表达式,以封装该子查询的结果
-- CTE to calculate average order total
-- with the name for the CTE (avg_order) and column (total)
WITH avg_order(total) AS (
-- CTE query
SELECT
AVG(total)
FROM
orders
WHERE
-- exclude test orders
product_id > 10
AND -- exclude orders before launch
created_at > '2016-04-21'
AND -- exclude test accounts
user_id > 10
)
-- our main query:
-- orders with above-average totals
SELECT
o.id,
o.total
FROM
orders AS o
-- join the CTE: avg_order
LEFT JOIN avg_order AS a
WHERE
-- total is above average
o.total > a.total
ORDER BY
o.total DESC
CTE 将查找平均值的逻辑打包起来,并将该逻辑与核心查询分开:查找总数高于平均值的订单 ID。请注意,此 CTE 的结果未保存在任何地方;每次运行查询时都会执行其子查询。
将此查询存储为 CTE 也使查询更易于修改。假设我们还想知道哪些订单具有
- 高于平均总数,
- 低于平均数量的已订购商品。
我们可以轻松地扩展查询,如下所示
-- CTE to calculate average order total and quantity
WITH avg_order(total, quantity) AS (
SELECT
AVG(total),
AVG(quantity)
FROM
orders
WHERE
-- exclude test orders
product_id > 10
AND -- exclude orders before launch
created_at > '2016-04-21'
AND -- exclude test accounts
user_id > 10
)
-- orders with above-average totals
SELECT
o.id,
o.total,
o.quantity
FROM
orders AS o -- join the CTE avg_order
LEFT JOIN avg_order AS a
WHERE
-- above-average total
o.total > a.total
-- below-average quantity
AND o.quantity < a.quantity
ORDER BY
o.total DESC,
o.quantity ASC
我们还可以选择并仅运行 CTE 中的子查询。
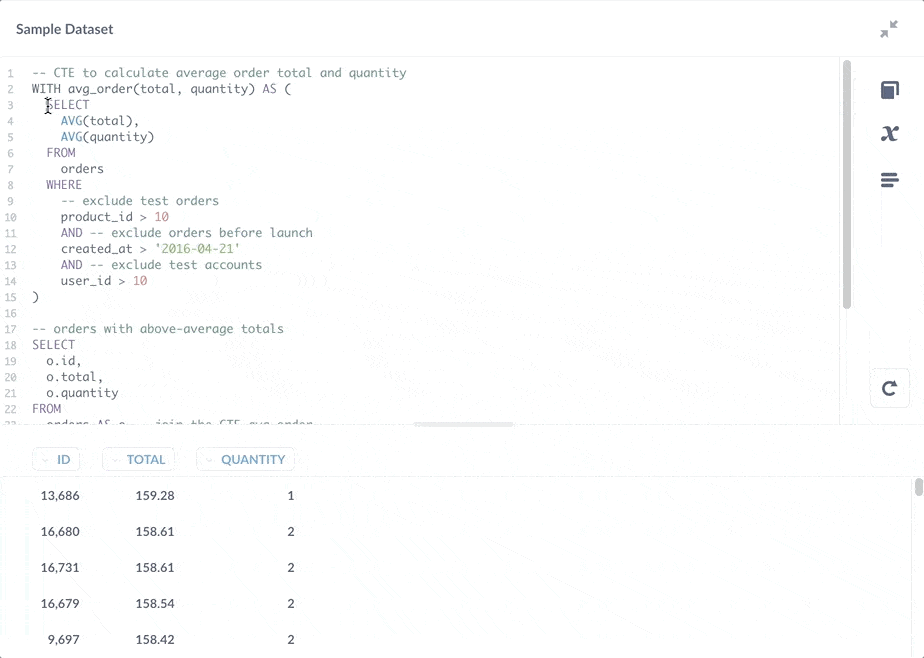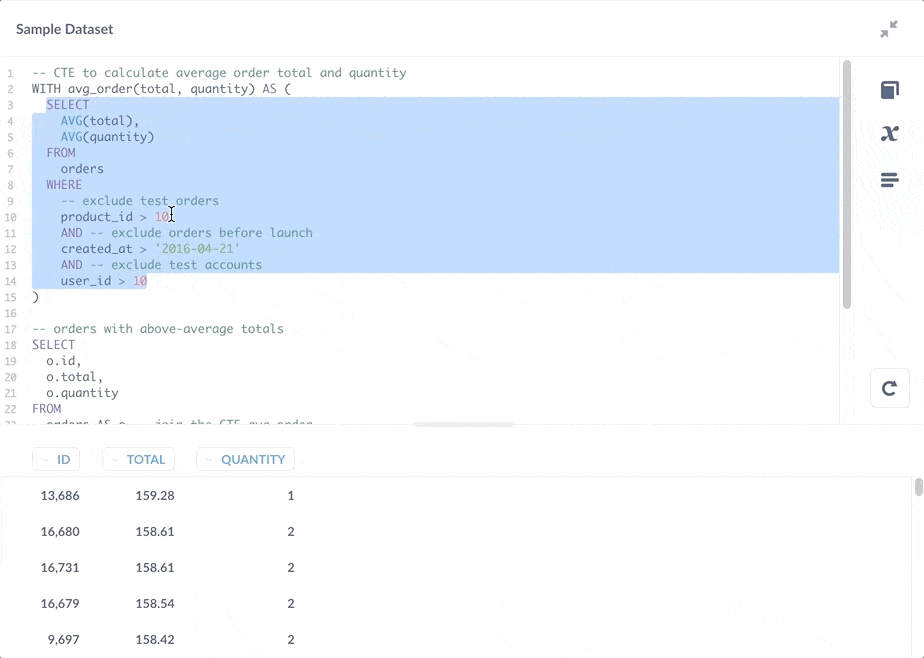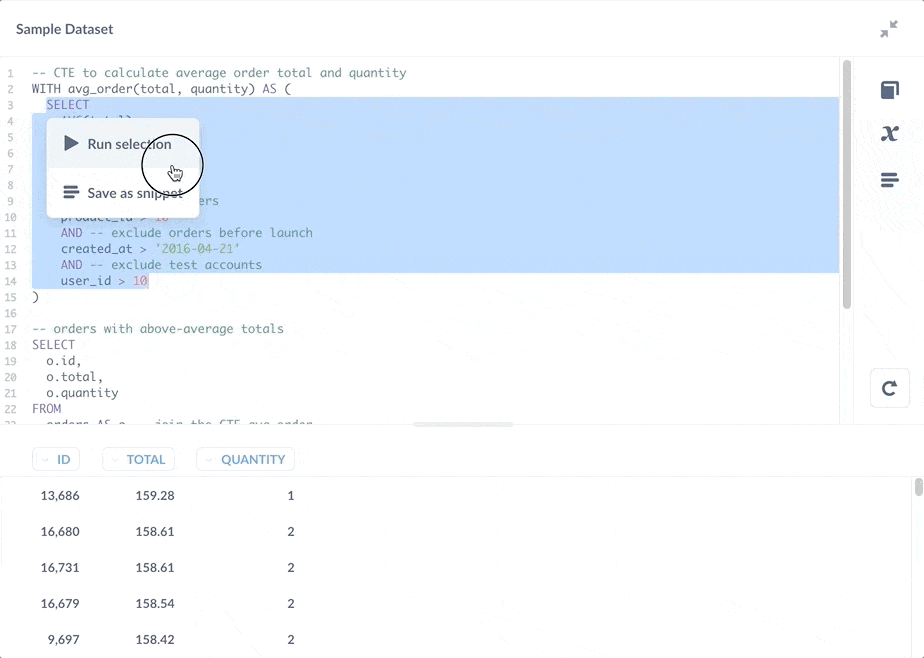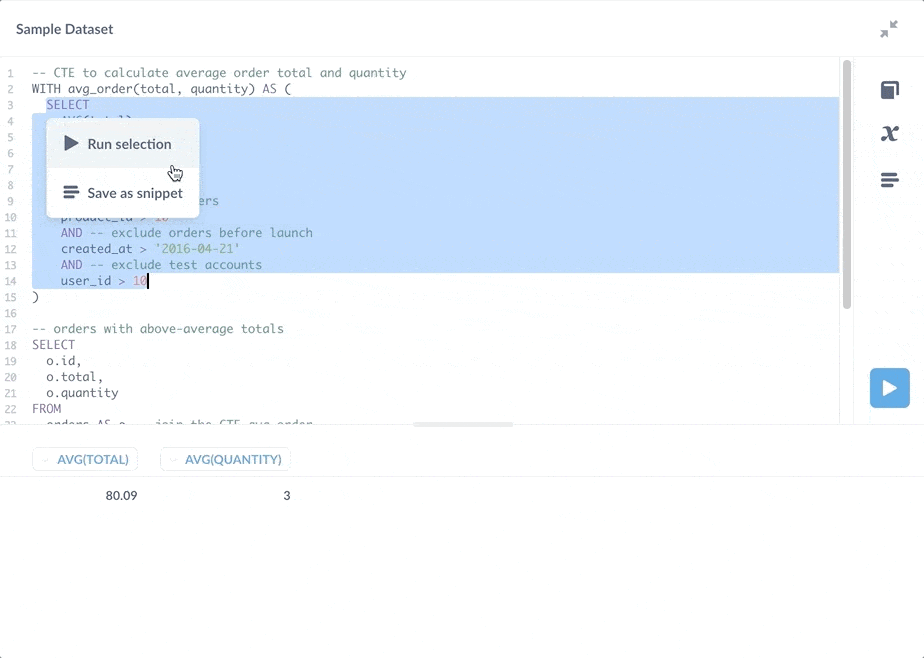
如上图所示,您还可以将 CTE 的子查询保存为 片段,但将子查询保存为问题会更好。决定片段和已保存问题之间权衡的经验法则是,如果一段代码可以独立返回结果,您可能需要考虑将其保存为问题(请参阅 片段与已保存问题与视图)。
Snippet 的更好用例是捕获过滤客户订单逻辑的 WHERE 子句。
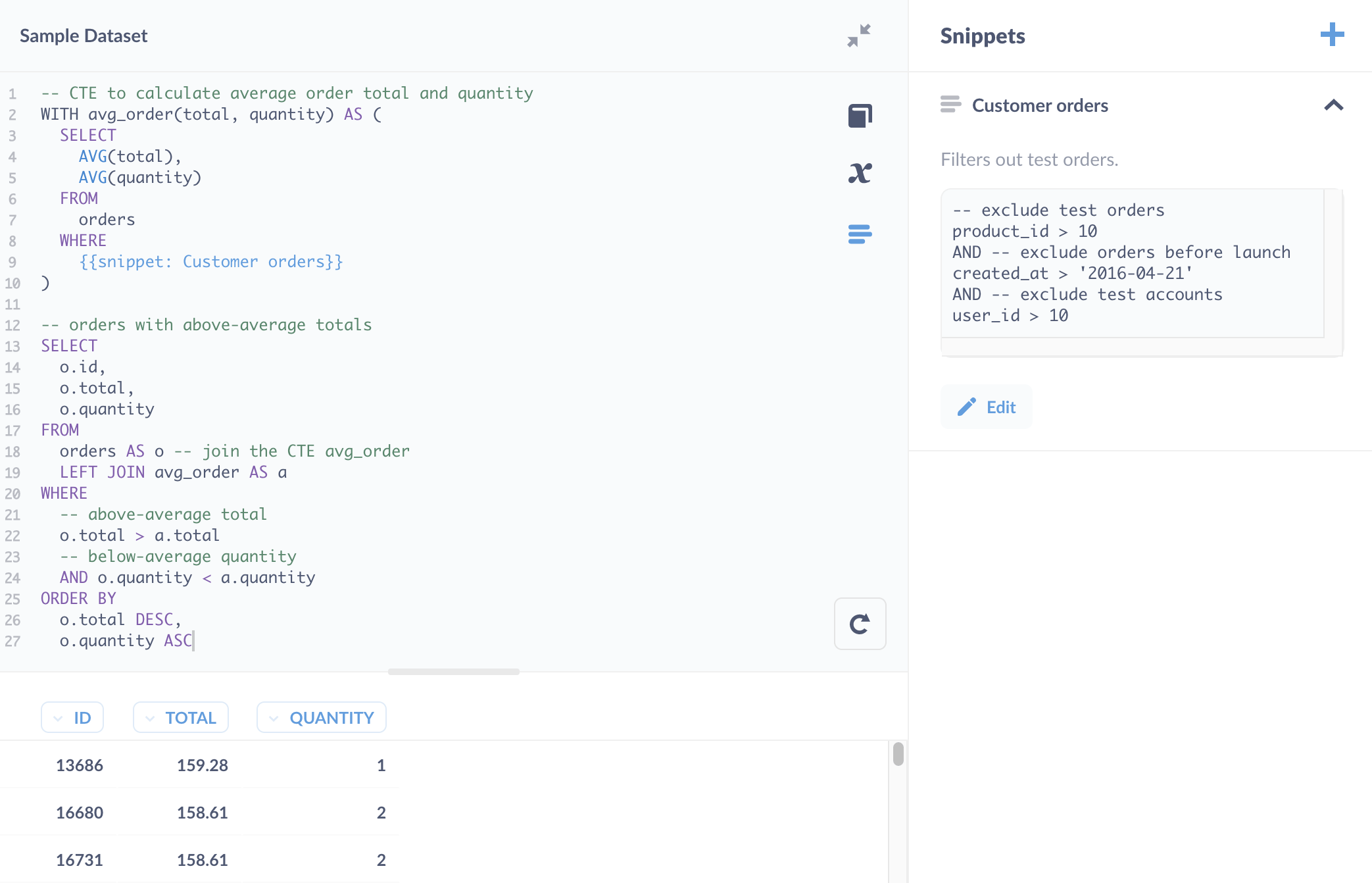
使用已保存问题的 CTE
您可以使用 WITH 语句来引用已保存的问题
WITH avg_order(total, quantity) AS {{#2}}
-- orders with above-average totals
SELECT
o.id,
o.total,
o.quantity
FROM
orders AS o -- join the CTE avg_order
LEFT JOIN avg_order AS a
WHERE
-- above-average totals
o.total > a.total
-- below-average quantity
AND o.quantity < a.quantity
ORDER BY
o.total DESC,
o.quantity ASC
您可以使用变量侧边栏查看由变量 {{#2}} 引用的问题。在这种情况下,2 是问题的 ID。
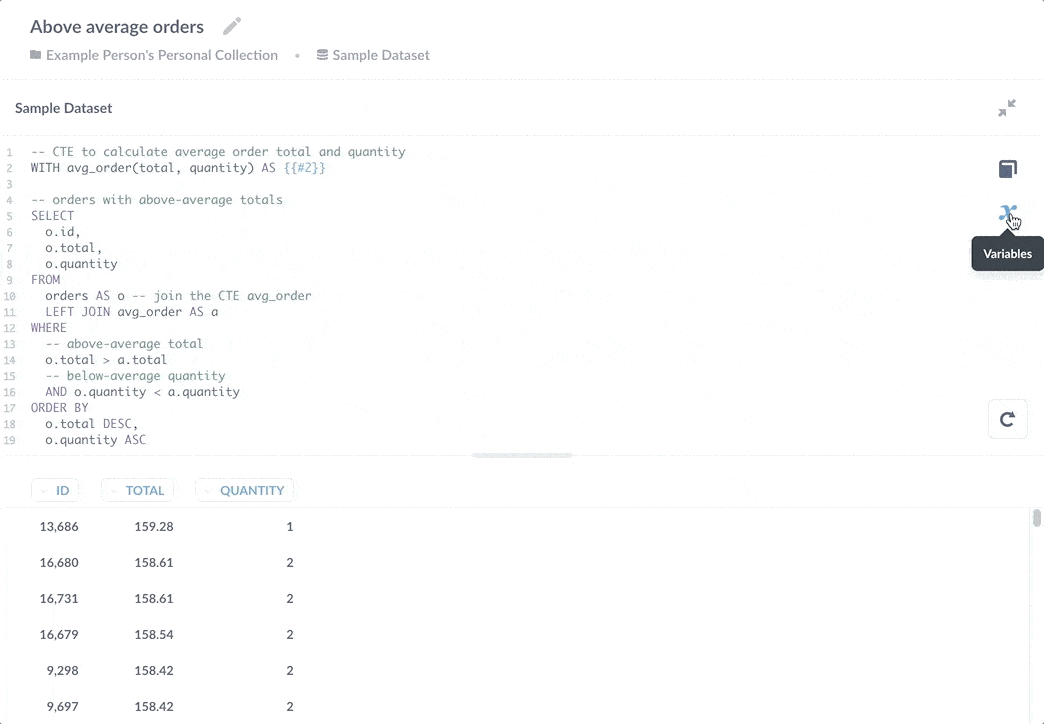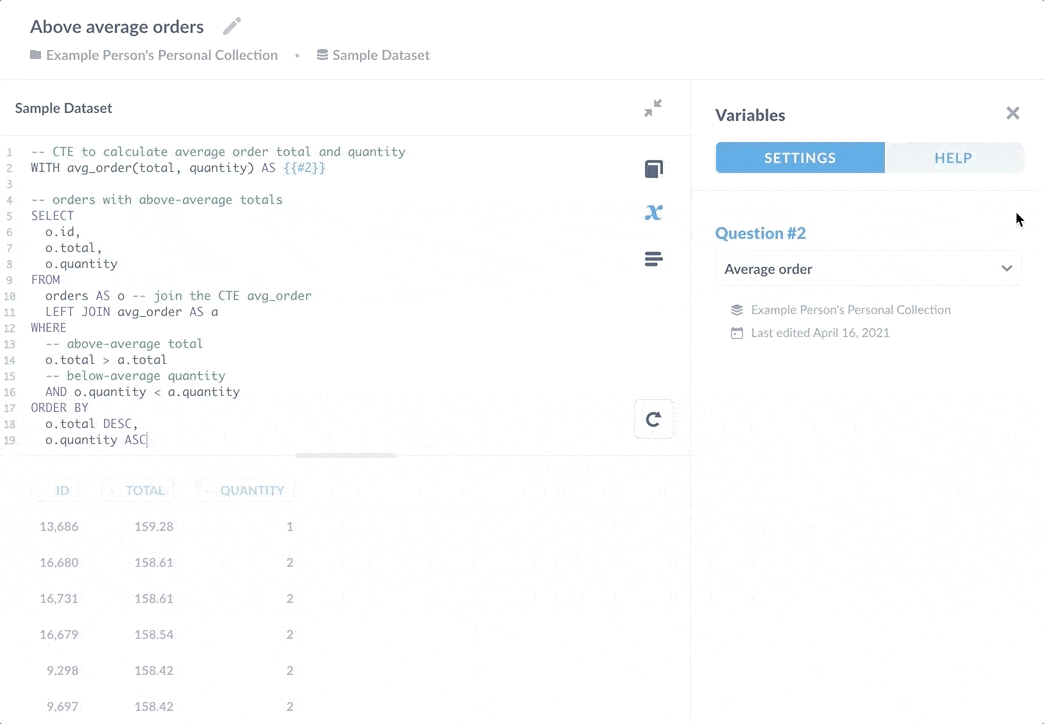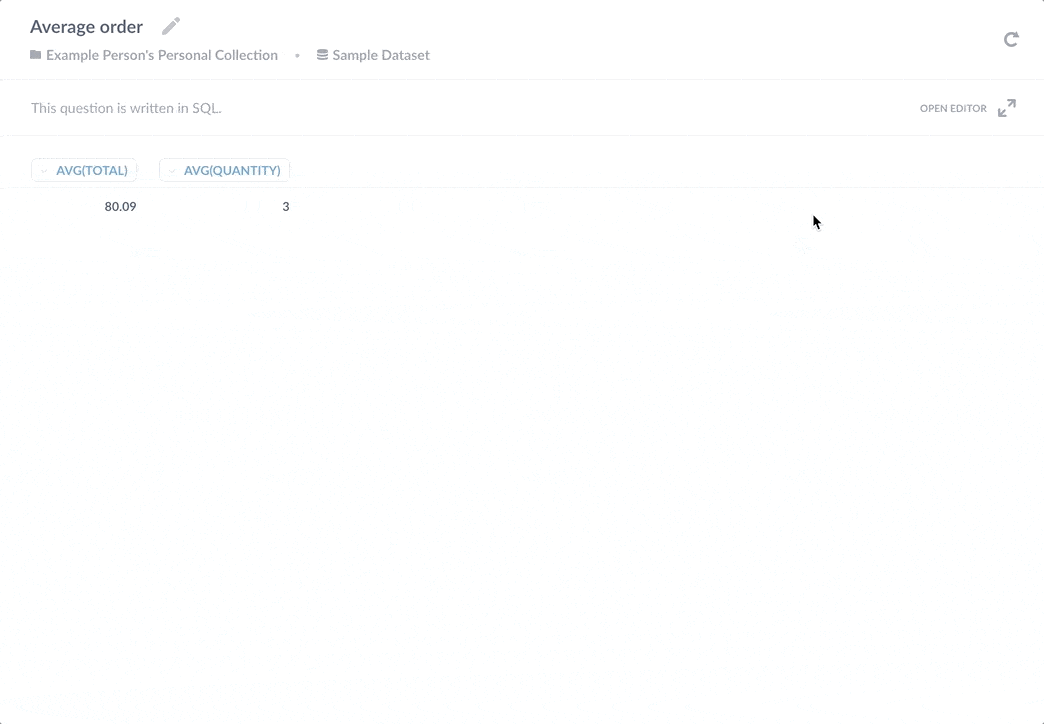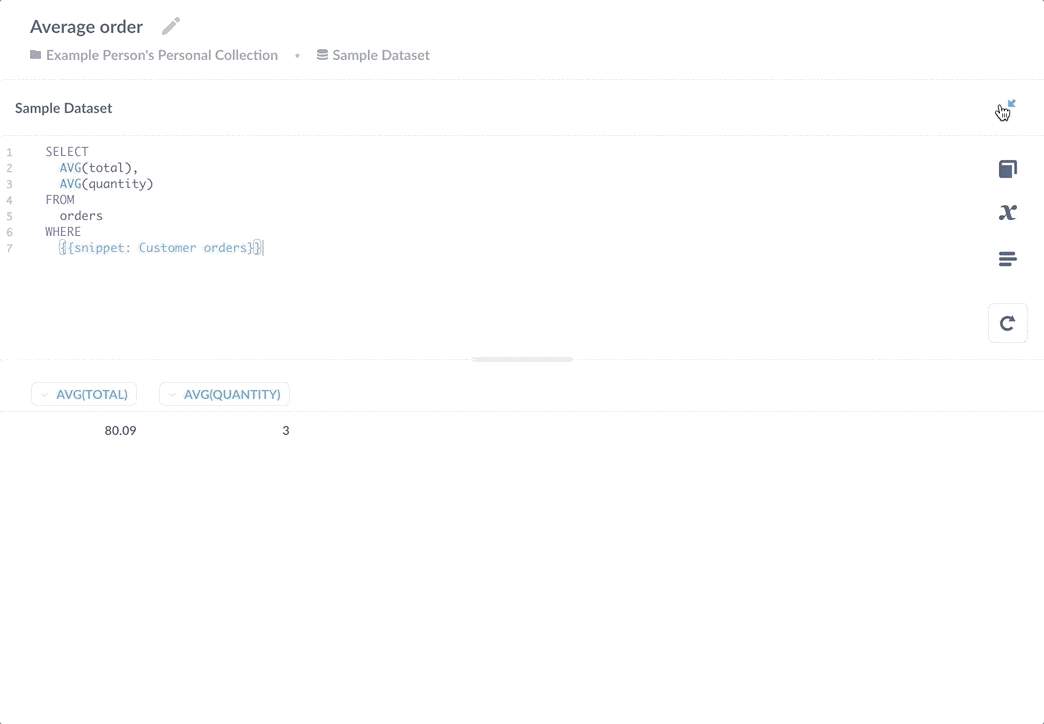
通过将该子查询保存为独立问题,多个问题可以引用其结果。如果您需要添加额外的 WHERE 子句来排除更多测试订单的计算,每个引用该计算的问题都将受益于更新。这种好处的另一面是,如果您更改了已保存问题以返回不同的列,它将破坏依赖于其结果的查询。
用于多级聚合的 CTE
您可以使用 CTE 来执行多级或多阶段聚合。也就是说,您可以对聚合进行聚合,例如计算计数的平均值。
示例:每个产品类别每周的平均订单数量是多少?
为了回答本节标题中的问题,我们需要
- 计算每个产品类别每周的订单数量。
- 计算每个类别的平均数量。
您可以使用 CTE 来计算数量,然后使用主查询来计算平均值。
-- CTE to find orders per week by product category
WITH orders_per_week(
order_week, order_count, category
) AS (
SELECT
DATE_TRUNC('week', o.created_at) as order_week,
COUNT(*) as order_count,
category
FROM
orders AS o
left join products AS p ON o.product_id = p.id
GROUP BY
order_week,
p.category
)
-- Main query to calculate average order count per week
SELECT
category AS "Category",
AVG(order_count) AS "Average orders per week"
FROM
orders_per_week
GROUP BY
category
结果为
|Category |Average orders per week|
|---------|-----------------------|
|Doohickey|19 |
|Gizmo |23 |
|Widget |25 |
|Gadget |24 |
查询构建器中的多级聚合
为了提供此查询背后逻辑的概览,上述查询在 Metabase 的查询构建器中看起来是这样的
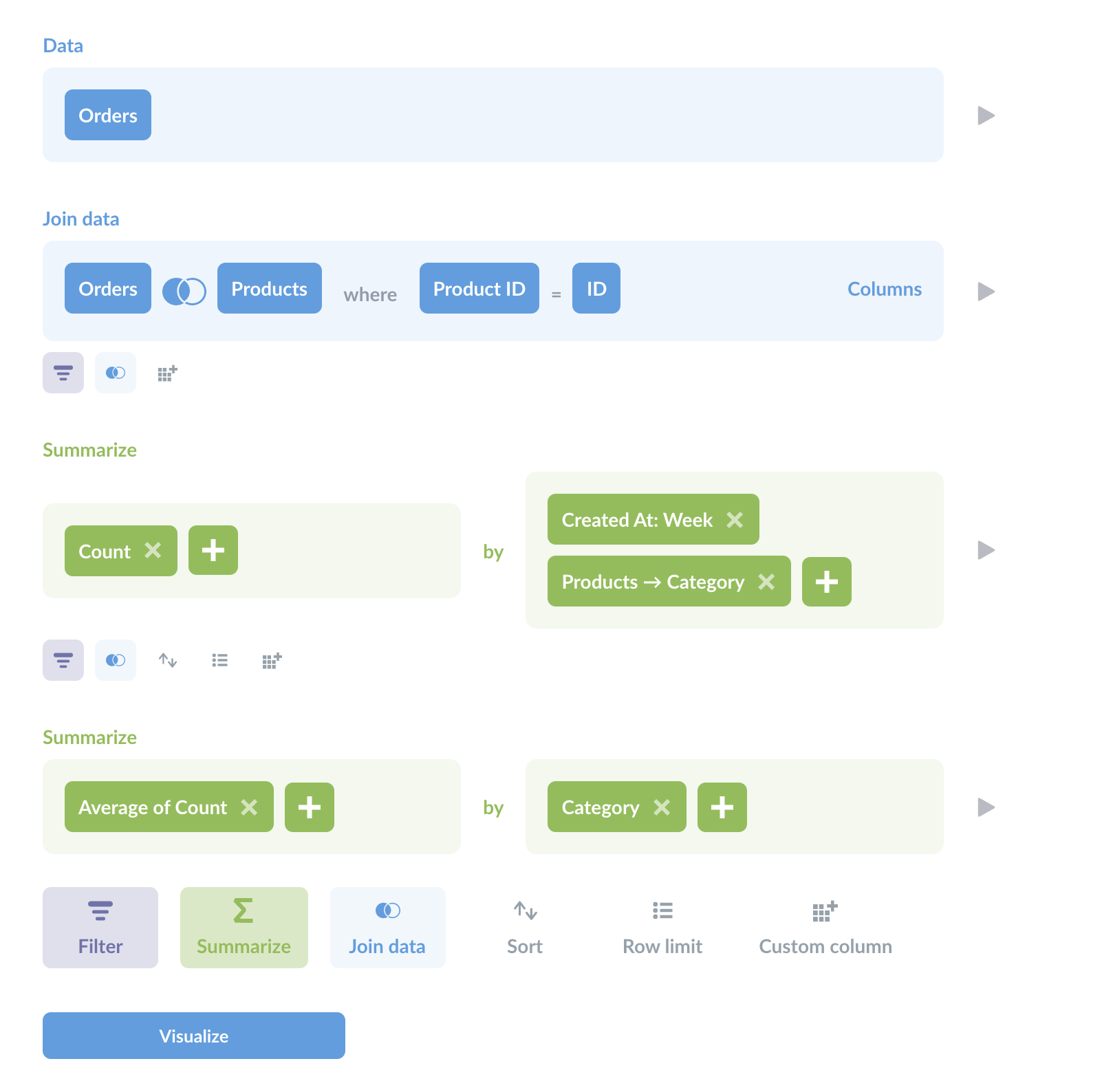
您可以看到两个聚合阶段(两个汇总部分)。如您所见,即使您正在编写 SQL 查询,查询构建器也是探索数据并帮助您规划方法的绝佳工具。
在单个查询中使用多个 CTE
您可以在同一查询中使用多个 CTE。您只需用逗号分隔它们的名称和子查询,如下所示
-- first CTE
WITH avg_order(total) AS (
SELECT
AVG(total)
FROM
orders
),
-- second CTE (note the preceding comma)
avg_product(rating) AS (
SELECT
AVG(rating)
FROM
products
)
阅读
您可以在我们关于 SQL 中的日期处理的文章中查看更多 CTE 的实际应用,包括一个使用 CTE 连接到自身的示例。

